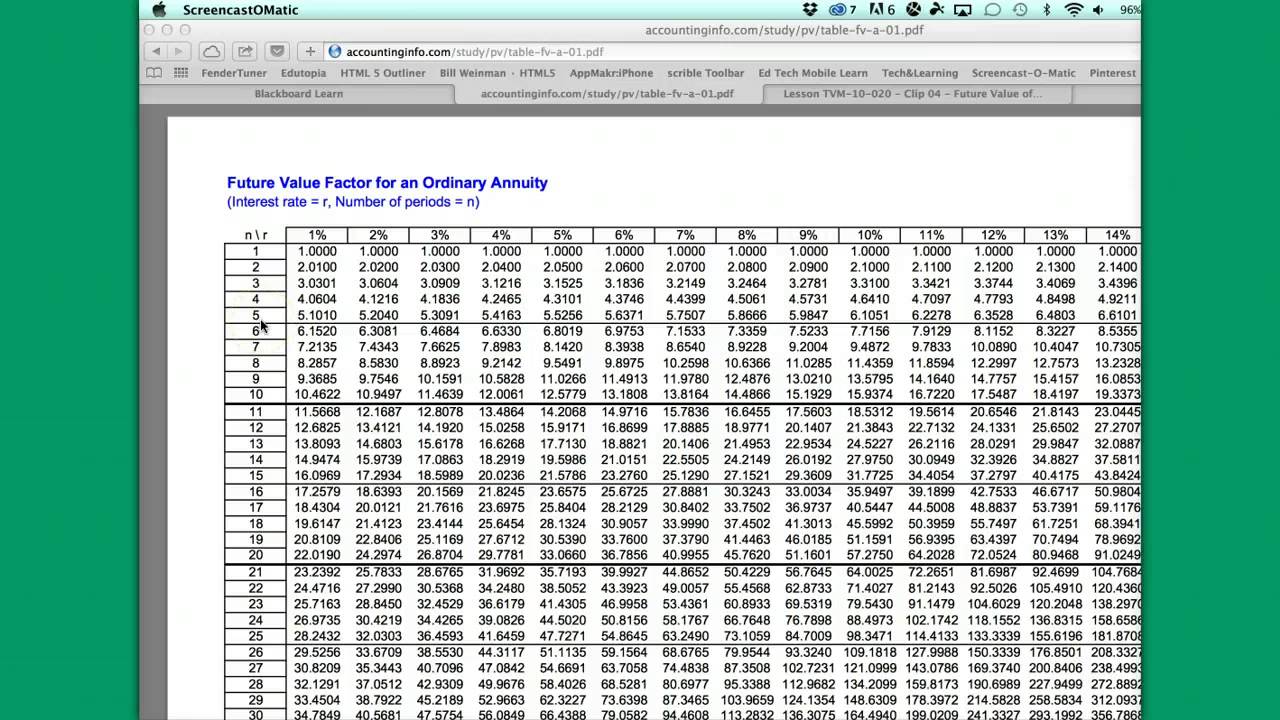
Since this kind of annuity is paid only under a specific condition (i.e., the annuitant is still alive), it is known as a contingent annuity. If the contract defines the period in advance, we call it a certain or guaranteed annuity. A wide range of financial products all involve a series of payments that are equal and are made at fixed intervals. The two conditions that need to be met are constant payments and a fixed number of periods. For example, $500 to be paid at the end of each of the next five years is a 5-year annuity.
How is the PV of Annuity Formula derived?
The reason the values are higher is that payments made at the beginning of the period have more time to earn interest. For example, if the $1,000 was invested on January 1 rather than January 31, it would have an additional month to grow. As mentioned, an annuity due differs from an ordinary annuity in that the annuity due’s payments are made at the beginning, rather than the end, of each period. You can calculate the present or future value for an ordinary annuity or an annuity due using the formulas shown below. To learn more about or do calculations on future value instead, feel free to pop on over to our Future Value Calculator.
Learn
You can notice that for a positive discount rate, the future value (FV – future value calculator) is always higher or equal to the present value (PV). Since an annuity’s present value depends on how much money you expect to receive in the future, you should keep the time value of money in mind when calculating the present value of your annuity. Financial calculators also have the ability to calculate politico analysis these for you, given the correct inputs. With ordinary annuities, payments are made at the end of a specific period. The difference affects value because annuities due have a longer amount of time to earn interest. These recurring or ongoing payments are technically referred to as annuities (not to be confused with the financial product called an annuity, though the two are related).
- Note that the calculator will convert the annual discount rate to the rate that corresponds to the payment frequency.
- This Present Value Calculator makes the math easy by converting any future lump sum into today’s dollars so that you have a realistic idea of the value received.
- Treasury bonds are generally considered to be the closest thing to a risk-free investment, so their return is often used for this purpose.
- Read on to learn how to calculate the present value (PV) or future value (FV) of an annuity.
- The present value of an annuity is the current value of future payments from an annuity, given a specified rate of return, or discount rate.
Present Value Calculator – NPV
Present Value, or PV, is defined as the value in the present of a sum of money, in contrast to a different value it will have in the future due to it being invested and compound at a certain rate. While most annuities will compound periodically, others will compound continuously. You can learn more about compound interest with our compound interest calculator.
If you chose to enter a future lump sum, this result represents the periodic payment amount needed to pay off the loan within the specified time period. The present value (PV) of an annuity is the discounted value of the bond’s future payments, adjusted by an appropriate discount rate, which is necessary because of the time value of money (TVM) concept. The present value of an annuity is the total value of all of future annuity payments. A key factor in determining the present value of an annuity is the discount rate. This can be an expected return on investment or a current interest rate.
How To Calculate The Value Of An Annuity
For a brief, educational introduction to finance and the time value of money, please visit our Finance Calculator. The Present Value of Annuity calculation can be used to determine the value of a variety of different annuities. To make it easier to understand the results of the calculation, we have divided them into different categories, based on the value of the annuity. The table below shows the annual present values for each year of this annuity. While you would receive a total of $10,000, the present value is $7,721.73 because it is discounted each year using the 5% interest rate.
This would aid them in making sound investment decisions based on their anticipated needs. However, external economic factors, such as inflation, can adversely affect the future value of the asset by eroding its value. Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, so the person would come out ahead by choosing the lump-sum payment over the annuity. The FV of money is also calculated using a discount rate, but extends into the future. Present value calculations can also be used to compare the relative value of different annuity options, such as annuities with different payment amounts or different payment schedules.
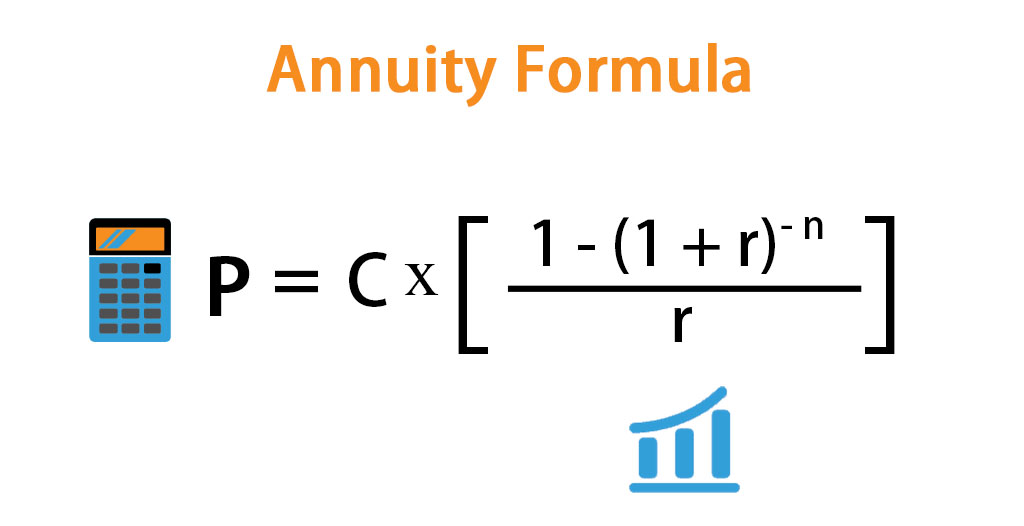
Annuities are further differentiated depending on the variability of their cash flows. There are fixed annuities, where the payments are equal, but also variable annuities, that you allow to accumulate and then invest based on several, tax-deferred options. You may also find equity-indexed annuities, where payments are adjusted by an index. If you are trying to assess whether a particular investment will bring you profit in the long term, this NPV calculator is a tool for you. Based on your initial investment and consecutive cash flows, it will determine the net present value, and hence the profitability, of a planned project.
With these two concepts in hand, we will now learn to amortize a loan, and to find the present value of an annuity. Choose whether you want to enter a future lump sum or a payment amount, and enter the corresponding amount. Earlier cash flows can be reinvested earlier and for a longer duration, so these cash flows carry the highest value (and vice versa for cash flows received later). Using the present value formula helps you determine how much cash you must earmark for an annuity to reach your goal of how much money you’ll receive in retirement. An annuity’s value is the sum of money you’ll need to invest in the present to provide income payments down the road.

Leave a comment